Trends and Cycles in China’s Macroeconomy
China’s spectacular growth over the 2000s has slowed since 2013. The driving force behind the country’s growth was investment, so the key to understanding the slowdown lies in understanding what sustained investment in the past. This column shows how a preferential credit policy promoting heavy industrialisation explains the trends and cycles in China’s macroeconomy over the past two decades. This policy was not without negative consequences, particularly in terms of the distortions it introduced for business finance. Going forward, China needs to focus on creating the right incentives for banks to make loans to small productive businesses.
Growth has been the hallmark for China. In recent years, however, China’s GDP growth has slowed down considerably while countercyclical government policy has taken center stage. Never has this change been more true than after the 2008 financial crisis, when the government injected 4 trillion RMBs into investment to combat the sharp fall of output growth. Issues related to both trend and cycle are now on the minds of policymakers and economists.
The key issue for China today is the slowdown of GDP growth since 2013 (see, for example, the article “Prudence Without a Purpose” in the 5 July 2015 issue of The Economist, and the article “China Growth Lowest Since 2009 as Property and Manufacturing Drag” in the 5 July 2015 issue of Financial Times). What causes such a growth slowdown? The data indicate that much of the slowdown is the slowdown of investment, which has been the driving force of China’s growth since 1997. To understand why investment in China has recently slowed down, we must understand what has sustained investment growth in the past.
Explaining China’s growth
Song, Storesletten, and Zilibotti (2011) explain China’s spectacular growth trend in the 2000s. They construct a model economy with heterogeneous firms that differ in both productivity and access to the credit market to explain the observed coexistence of sustained returns to capital and growing foreign surpluses in China in most of the 2000s. Their model replicates the observed disinvestment of state-owned enterprises (SOEs) in the labor-intensive sector as private-owned enterprises (POEs) accumulate capital in the same sector. In this two-sector model, they characterize two transition stages. In the first stage, both SOEs and POEs coexist in the labor-intensive sector, while capital-intensive goods is produced exclusively by SOEs. In the second stage, SOEs disappear from the labor-intensive sector and POEs become the sole producers in that productive sector. Song, Storesletten, and Zilibotti (2011) present a persuasive story about resource reallocations between SOEs and POEs within the productive labor-intensive sector, which is identified as the source of total factor productivity (TFP) growth since the late 1990s.
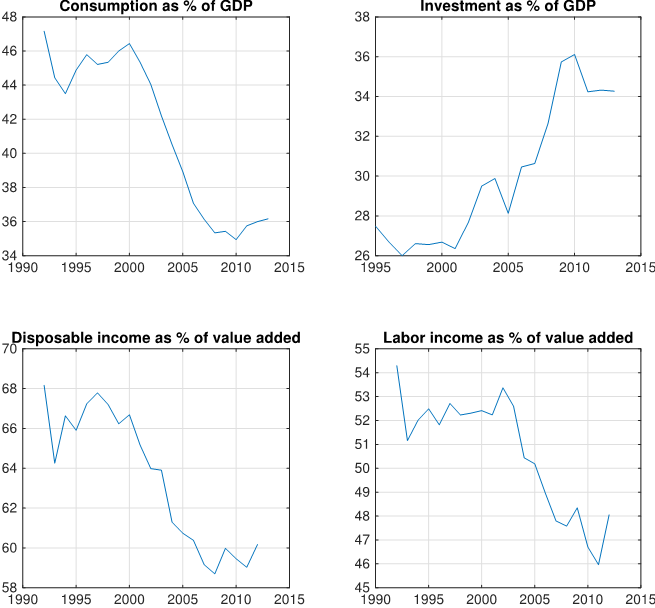
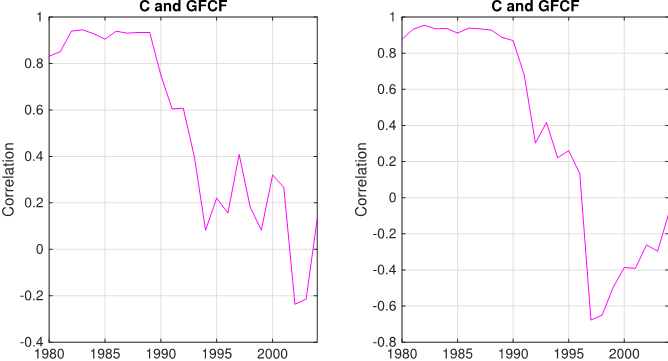
Although discussions around SOEs versus POEs have dominated the literature on China, the SOE-POE classification does not help explain the rising investment rate, the decline of labor income share, and the weak or negative cyclical comovement between investment and consumption or between investment and labor income. Figure 1 displays the recent trend patterns in China: investment as a share of GDP has steadily increased, while household consumption as a share of GDP and the labor income (as well as household disposable income) as a share of total value added have steadily declined. Against a backdrop of these unbalanced trends is a stark picture of a structural break of the correlation between investment and consumption. As shown in Figure 2, the strong positive correlation between investment and household consumption breaks down in the late 1990s, whether it is measured by annual growth rates or HP-filtered series.
According to Acemoglu and Guerrieri (2008), Fernald and Neiman (2011), and Chang and Hornstein (2015), a combination of two conditions may explain a rising investment rate and a declining share of labor income: the TFP in heavy industries must grow faster than in light industries and the relative price of investment goods must decline. For the Chinese economy, there is no evidence in support of these two conditions. In fact, since the late 1990s, the deepening of capital, not TFP growth, has become the major source of GDP growth in China.
Buera and Shin (2013) study the investment boom experienced by other fast growing economies (e.g. Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore). In those economies, resources gradually move from unproductive firms to productive firms, so that the saving (investment) rate increases during the reallocation phase. At the same time, the labor income share increased or remained stable during the investment boom period. China is different. Much of the investment boom was at a cost of labor income growth and consumption growth. Therefore, unless much of the investment income is channeled to households for their labor inputs, the investment boom is unsustainable in the long run.
Resource allocations
To address these key China's macroeconomic issues in one coherent and tractable framework, a recent paper by Chang, Chen, Waggoner, and Zha (2016) takes a different perspective by shifting an emphasis to resource reallocations between the heavy and light sectors. Thestriking facts about both trends and cycles in China indicate that something fundamental has changed since the late 1990s. We argue that these changes began in March 1996, when the Eighth National People’s Congress passed a historic long-term plan to adjust the industrial structure for the next 15 years in favor of strengthening heavy industries. Since March 1996, the government has been actively promoting what is called “heavy industries,” which are largely composed of big capital-intensive industries such as infrastructure, real estate, basic industries (metal products, autos, and high-tech machinery), and other heavy industries (petroleum and telecommunication). The promotion has been supported by medium-term and long-term bank loans giving priority to the heavy sector. The other industries, more labor intensive and called “light industries,” do not receive the same preferential treatment. Our approach is to build a two-sector model with a special emphasis on resource and credit reallocations between the heavy and light sectors and by introducing two new institutional ingredients into themodel: a collateral constraint on producers in the heavy sector and a lending friction in the banking sector. With these new ingredients their model can replicate both the trend patterns and the cyclical patterns displayed in Figures 1 and 2.
Problems with preferential policy
The central policy message is that the spectacular economic growth in China is not an unalloyed progress as it begets the debt problem faced by China today. We argue that preferential credit policy for promoting heavy industries accounts for the unusual cyclical patterns as well as the post-1990s economic transition featured by the persistently rising investment rate, the declining labor income share, and a growing foreign surplus.
Such a preferential policy, however, distorts business finance and entails negative consequences. Under the central government’s strategic plan of promoting heavy industries, local governments have made implicit guarantees of long-term bank loans to heavy industries, most of which are capital-intensive large firms and are less productive than the vibrant small businesses. This is what we call “Green Banking.” The result is fast growth, but the growth is unbalanced and at the cost of low consumption and low labor income.
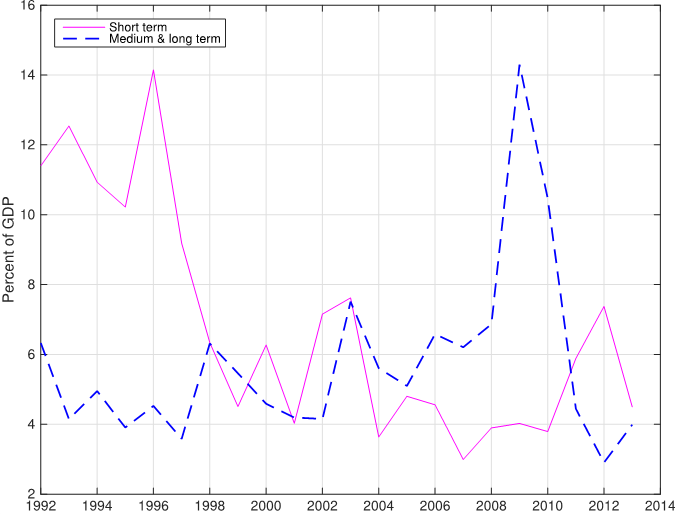
The easy credit policy for promoting heavy industries crowds out short-term loans to productive small firms. As a result, short-term loans are priced too high because they are not guaranteed by the government. We call this short-term lending “Yellow Banking.” Indeed, the Chinese data supports this crowding-out effect implied by the model. Figure 3 shows that new medium-term and long-term loans move negatively with new short-term bank loans. The average correlation between the two types of loans is -0.4. This negative correlation is most conspicuous right after the 2008 financial crisis, when the government injected massive credits into medium-term and long-term investment projects with a spike of new long-term loans to blunt the impact on China of the severe global recession, while new short-term loans were left unchanged. When this prodigious government credit expansion ceased in 2010, new short-term loans began to rise.
Going forward
Financial reforms in China should focus on Green Banking. Only when the practice of Green Banking is properly reformed would commercial banks have incentives to make loans to small and productive businesses. The stake cannot be higher. The Eighteenth National People's Congress, when discussing various policy goals in 2012, explicitly expressed concerns about low consumption growth and low labor share of income in China. In addition, a rapid run-up in China’s corporate debts and local government debtsas a result of the preferential credit policy toward heavy industries has now reached a level that deems unsustainable. Thus, China’s macroeconomy faces the twin problems: (a) low consumption and income growth and (b) overcapacity of heavy industries with rising debt risks. How to resolve these problems might have profound policy implications. Because both problems have stemmed from a preferential credit policy for promoting the heavy industrialization since the late 1990s, an effective policy would aim at reducing the preferential credit access given to large firms and especially those in heavy industries. In short, financial reforms geared for eliminating such a distortion would go a long way toward making both short-term and long-term loans function efficiently and putting the economy on a more balanced path.
Authors’ note: This article is a reprint with minor revisions from the VoxEU article published at https://voxeu.org/article/trends-and-cycles-china-s-macroeconomy. The authors are grateful to the permission given by VoxEU.org to publish this article. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta or the Federal Reserve System.
Acemoglu, D. and V. Guerrieri (2008): “Capital Deepening and Nonbalanced Economic Growth,” Journal of Political Economy, 116, 467–498.
Buera F. J. and Y. Shin (2013): “Financial Frictions and the Persistence of History: A Quantitative Exploration,” Journal of Political Economy, 121, 221–272.
Chang, Y. and A. Hornstein (2015): “Transition Dynamics in the Neoclassical Growth Model: The Case of South Korea,” The B.E. Journal of Macroeconomics, Forthcoming.
Chang, C., K. Chen, D. Waggoner, and T. Zha (2016): “Trends and Cycles in China’s Macroeconomy,” 30th NBER Macroeconomics Annual.
Fernald, J. and B. Neiman (2011): “Growth Accounting with Misallocation: Or, Doing Less with More in Singapore,” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 3, 29–74.
Growth has been the hallmark for China. In recent years, however, China’s GDP growth has slowed down considerably while countercyclical government policy has taken center stage. Never has this change been more true than after the 2008 financial crisis, when the government injected 4 trillion RMBs into investment to combat the sharp fall of output growth. Issues related to both trend and cycle are now on the minds of policymakers and economists.
The key issue for China today is the slowdown of GDP growth since 2013 (see, for example, the article “Prudence Without a Purpose” in the 5 July 2015 issue of The Economist, and the article “China Growth Lowest Since 2009 as Property and Manufacturing Drag” in the 5 July 2015 issue of Financial Times). What causes such a growth slowdown? The data indicate that much of the slowdown is the slowdown of investment, which has been the driving force of China’s growth since 1997. To understand why investment in China has recently slowed down, we must understand what has sustained investment growth in the past.
Explaining China’s growth
Song, Storesletten, and Zilibotti (2011) explain China’s spectacular growth trend in the 2000s. They construct a model economy with heterogeneous firms that differ in both productivity and access to the credit market to explain the observed coexistence of sustained returns to capital and growing foreign surpluses in China in most of the 2000s. Their model replicates the observed disinvestment of state-owned enterprises (SOEs) in the labor-intensive sector as private-owned enterprises (POEs) accumulate capital in the same sector. In this two-sector model, they characterize two transition stages. In the first stage, both SOEs and POEs coexist in the labor-intensive sector, while capital-intensive goods is produced exclusively by SOEs. In the second stage, SOEs disappear from the labor-intensive sector and POEs become the sole producers in that productive sector. Song, Storesletten, and Zilibotti (2011) present a persuasive story about resource reallocations between SOEs and POEs within the productive labor-intensive sector, which is identified as the source of total factor productivity (TFP) growth since the late 1990s.
Although discussions around SOEs versus POEs have dominated the literature on China, the SOE-POE classification does not help explain the rising investment rate, the decline of labor income share, and the weak or negative cyclical comovement between investment and consumption or between investment and labor income. Figure 1 displays the recent trend patterns in China: investment as a share of GDP has steadily increased, while household consumption as a share of GDP and the labor income (as well as household disposable income) as a share of total value added have steadily declined. Against a backdrop of these unbalanced trends is a stark picture of a structural break of the correlation between investment and consumption. As shown in Figure 2, the strong positive correlation between investment and household consumption breaks down in the late 1990s, whether it is measured by annual growth rates or HP-filtered series.
Figure 1: China’s trend patterns in the last two decades

Figure 2: Time series of correlations with the 10-year moving window. The left-column graph represents the correlation of annual growth rates. The right-column graph reports the correlation of HP-filtered log annual values. “C” stands for household consumption; “GFCF” stands for gross fixed capital formation, which measures investment.

According to Acemoglu and Guerrieri (2008), Fernald and Neiman (2011), and Chang and Hornstein (2015), a combination of two conditions may explain a rising investment rate and a declining share of labor income: the TFP in heavy industries must grow faster than in light industries and the relative price of investment goods must decline. For the Chinese economy, there is no evidence in support of these two conditions. In fact, since the late 1990s, the deepening of capital, not TFP growth, has become the major source of GDP growth in China.
Buera and Shin (2013) study the investment boom experienced by other fast growing economies (e.g. Korea, Taiwan, and Singapore). In those economies, resources gradually move from unproductive firms to productive firms, so that the saving (investment) rate increases during the reallocation phase. At the same time, the labor income share increased or remained stable during the investment boom period. China is different. Much of the investment boom was at a cost of labor income growth and consumption growth. Therefore, unless much of the investment income is channeled to households for their labor inputs, the investment boom is unsustainable in the long run.
Resource allocations
To address these key China's macroeconomic issues in one coherent and tractable framework, a recent paper by Chang, Chen, Waggoner, and Zha (2016) takes a different perspective by shifting an emphasis to resource reallocations between the heavy and light sectors. Thestriking facts about both trends and cycles in China indicate that something fundamental has changed since the late 1990s. We argue that these changes began in March 1996, when the Eighth National People’s Congress passed a historic long-term plan to adjust the industrial structure for the next 15 years in favor of strengthening heavy industries. Since March 1996, the government has been actively promoting what is called “heavy industries,” which are largely composed of big capital-intensive industries such as infrastructure, real estate, basic industries (metal products, autos, and high-tech machinery), and other heavy industries (petroleum and telecommunication). The promotion has been supported by medium-term and long-term bank loans giving priority to the heavy sector. The other industries, more labor intensive and called “light industries,” do not receive the same preferential treatment. Our approach is to build a two-sector model with a special emphasis on resource and credit reallocations between the heavy and light sectors and by introducing two new institutional ingredients into themodel: a collateral constraint on producers in the heavy sector and a lending friction in the banking sector. With these new ingredients their model can replicate both the trend patterns and the cyclical patterns displayed in Figures 1 and 2.
Problems with preferential policy
The central policy message is that the spectacular economic growth in China is not an unalloyed progress as it begets the debt problem faced by China today. We argue that preferential credit policy for promoting heavy industries accounts for the unusual cyclical patterns as well as the post-1990s economic transition featured by the persistently rising investment rate, the declining labor income share, and a growing foreign surplus.
Such a preferential policy, however, distorts business finance and entails negative consequences. Under the central government’s strategic plan of promoting heavy industries, local governments have made implicit guarantees of long-term bank loans to heavy industries, most of which are capital-intensive large firms and are less productive than the vibrant small businesses. This is what we call “Green Banking.” The result is fast growth, but the growth is unbalanced and at the cost of low consumption and low labor income.
The easy credit policy for promoting heavy industries crowds out short-term loans to productive small firms. As a result, short-term loans are priced too high because they are not guaranteed by the government. We call this short-term lending “Yellow Banking.” Indeed, the Chinese data supports this crowding-out effect implied by the model. Figure 3 shows that new medium-term and long-term loans move negatively with new short-term bank loans. The average correlation between the two types of loans is -0.4. This negative correlation is most conspicuous right after the 2008 financial crisis, when the government injected massive credits into medium-term and long-term investment projects with a spike of new long-term loans to blunt the impact on China of the severe global recession, while new short-term loans were left unchanged. When this prodigious government credit expansion ceased in 2010, new short-term loans began to rise.
Figure 3: New bank loans to
non-financial enterprises as a percent of GDP. The correlation between
the two types of loans is -0.403 for 1992-2012 and -0.405 for 2000-2012.

Financial reforms in China should focus on Green Banking. Only when the practice of Green Banking is properly reformed would commercial banks have incentives to make loans to small and productive businesses. The stake cannot be higher. The Eighteenth National People's Congress, when discussing various policy goals in 2012, explicitly expressed concerns about low consumption growth and low labor share of income in China. In addition, a rapid run-up in China’s corporate debts and local government debtsas a result of the preferential credit policy toward heavy industries has now reached a level that deems unsustainable. Thus, China’s macroeconomy faces the twin problems: (a) low consumption and income growth and (b) overcapacity of heavy industries with rising debt risks. How to resolve these problems might have profound policy implications. Because both problems have stemmed from a preferential credit policy for promoting the heavy industrialization since the late 1990s, an effective policy would aim at reducing the preferential credit access given to large firms and especially those in heavy industries. In short, financial reforms geared for eliminating such a distortion would go a long way toward making both short-term and long-term loans function efficiently and putting the economy on a more balanced path.
Authors’ note: This article is a reprint with minor revisions from the VoxEU article published at https://voxeu.org/article/trends-and-cycles-china-s-macroeconomy. The authors are grateful to the permission given by VoxEU.org to publish this article. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta or the Federal Reserve System.
(Chun Chang, Shanghai Advanced Institute of Finance, Shanghai Jiao Tong University; Kaiji Chen, Economics Department, Emory University and the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta; Daniel F. Waggoner, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta; Tao Zha, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta and Emory University.)
Acemoglu, D. and V. Guerrieri (2008): “Capital Deepening and Nonbalanced Economic Growth,” Journal of Political Economy, 116, 467–498.
Buera F. J. and Y. Shin (2013): “Financial Frictions and the Persistence of History: A Quantitative Exploration,” Journal of Political Economy, 121, 221–272.
Chang, Y. and A. Hornstein (2015): “Transition Dynamics in the Neoclassical Growth Model: The Case of South Korea,” The B.E. Journal of Macroeconomics, Forthcoming.
Chang, C., K. Chen, D. Waggoner, and T. Zha (2016): “Trends and Cycles in China’s Macroeconomy,” 30th NBER Macroeconomics Annual.
Fernald, J. and B. Neiman (2011): “Growth Accounting with Misallocation: Or, Doing Less with More in Singapore,” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 3, 29–74.
Song, Z., K. Storesletten, and F. Zilibotti (2011): “Growing Like China,” American Economic Review, 101, 196–233.

Latest
Most Popular
- VoxChina Covid-19 Forum (Second Edition): China’s Post-Lockdown Economic Recovery VoxChina, Apr 18, 2020
- China’s Great Housing Boom Kaiji Chen, Yi Wen, Oct 11, 2017
- China’s Joint Venture Policy and the International Transfer of Technology Kun Jiang, Wolfgang Keller, Larry D. Qiu, William Ridley, Feb 06, 2019
- The Dark Side of the Chinese Fiscal Stimulus: Evidence from Local Government Debt Yi Huang, Marco Pagano, Ugo Panizza, Jun 28, 2017
- Wealth Redistribution in the Chinese Stock Market: the Role of Bubbles and Crashes Li An, Jiangze Bian, Dong Lou, Donghui Shi, Jul 01, 2020
- Evaluating Risk across Chinese Housing Markets Yongheng Deng, Joseph Gyourko, Jing Wu, Aug 02, 2017
- What Is Special about China’s Housing Boom? Edward L. Glaeser, Wei Huang, Yueran Ma, Andrei Shleifer, Jun 20, 2017
- Privatization and Productivity in China Yuyu Chen, Mitsuru Igami, Masayuki Sawada, Mo Xiao, Jan 31, 2018
- How did China Move Up the Global Value Chains? Hiau Looi Kee, Heiwai Tang, Aug 30, 2017
- China’s Shadow Banking Sector: Wealth Management Products and Issuing Banks Viral V. Acharya, Jun Qian, Zhishu Yang, Aug 09, 2017




 Facebook
Facebook  Twitter
Twitter  Instagram
Instagram WeChat
WeChat  Email
Email 



